Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is a cornerstone in diabetes management, offering numerous benefits, especially for those who struggle with maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Over time, Metformin has gained significant popularity due to its efficacy and affordability, making it an essential part of diabetes care plans worldwide. In this article, we will explore the various uses of Metformin, highlight its pros and cons, and delve into a comparison with another medication often discussed in the diabetes treatment space: Metformin vs. Semaglutide.
Understanding Metformin’s Mechanism of Action
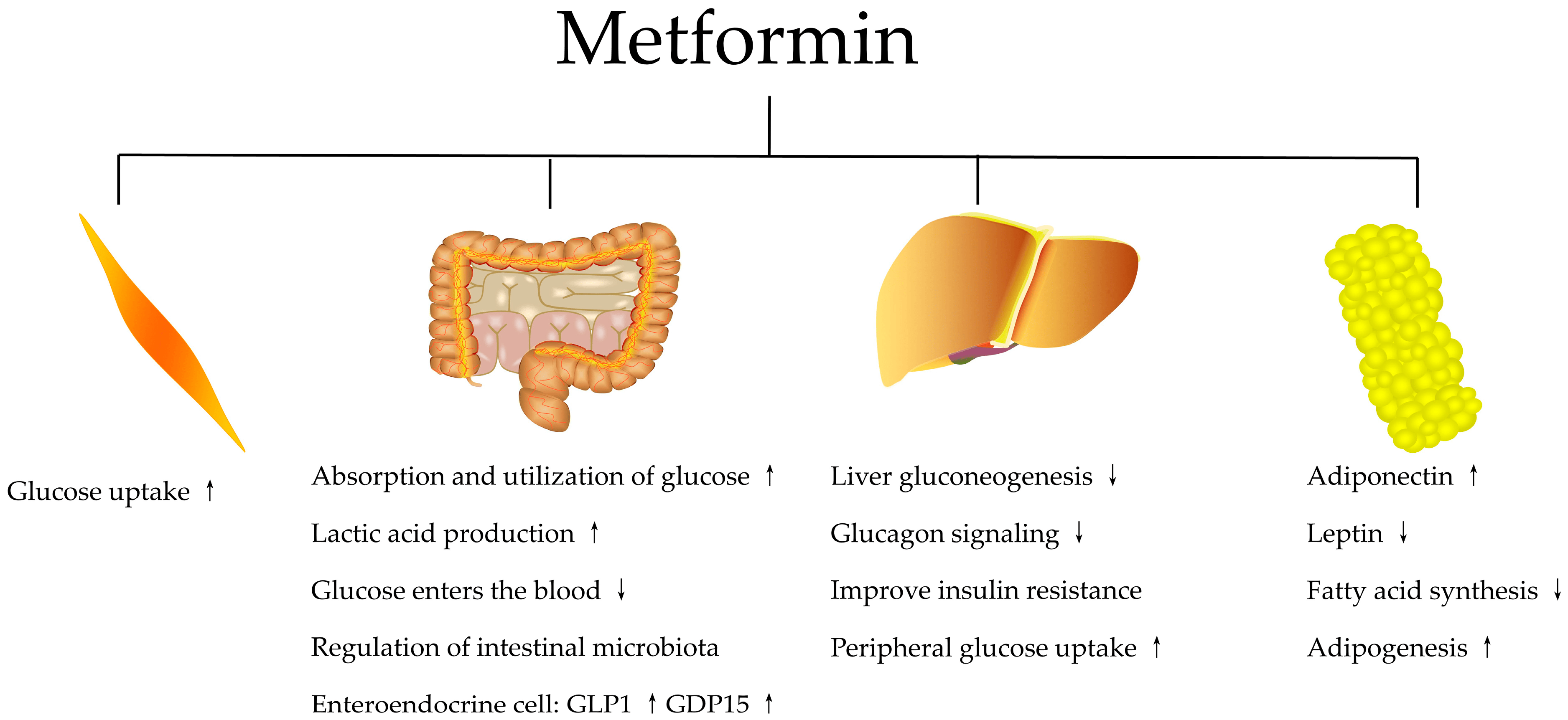
Metformin works by helping the body respond better to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Unlike many other diabetes medications, Metformin does not stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin, which helps reduce the risk of low blood sugar or hypoglycemia. Instead, it decreases the amount of sugar produced by the liver and helps improve insulin sensitivity in the muscles. This allows glucose to be utilized more effectively by the body, thus lowering blood sugar levels.
The mechanism of Metformin also extends beyond glucose control. It can have beneficial effects on weight management, making it an attractive option for individuals who struggle with obesity alongside diabetes. Many users find that Metformin can aid in modest weight loss, contributing to overall health improvements.
Pros and Cons of Metformin
When considering any medication, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons. Metformin is generally well-tolerated by most patients, and its long history of use in managing type 2 diabetes means there is a large body of evidence supporting its effectiveness.
Pros of Metformin
- Effective Blood Sugar Control: Metformin is highly effective in lowering blood sugar levels, which is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications such as nerve damage and heart disease.
- No Risk of Hypoglycemia: Unlike insulin or sulfonylureas, Metformin does not cause hypoglycemia, making it a safer option for long-term use.
- Weight Management: Many users report modest weight loss or at least weight stabilization when using Metformin, a significant benefit for those dealing with obesity.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Studies suggest that Metformin may have a protective effect on the heart, reducing the risk of heart-related complications in diabetic patients.
Cons of Metformin
- Gastrointestinal Side Effects: One of the most common drawbacks of Metformin is its gastrointestinal side effects, which can include nausea, diarrhea, and upset stomach. However, these symptoms often subside after the body adjusts to the medication.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Long-term use of Metformin has been associated with a risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. This can lead to fatigue and other health issues, so it’s important to monitor levels regularly.
- Not Effective for Type 1 Diabetes: Metformin is not suitable for individuals with type 1 diabetes, as it primarily works by improving insulin sensitivity, which is not the issue in type 1 diabetes.
Despite these cons, the benefits of Metformin for individuals with type 2 diabetes far outweigh the potential drawbacks, especially when used alongside lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
Metformin vs. Semaglutide: A Comparison
When comparing Metformin vs. Semaglutide, it’s important to understand that both medications are used to manage type 2 diabetes, but they work in different ways. Semaglutide is a newer drug in the GLP-1 receptor agonist class, and it offers a different mechanism of action compared to Metformin.
While Metformin primarily works by decreasing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity, Semaglutide mimics a hormone in the body that regulates insulin release and slows gastric emptying. This results in better control of blood sugar levels and can also lead to weight loss. Semaglutide has garnered attention for its ability to aid in significant weight reduction, which can be particularly beneficial for obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
However, Semaglutide comes with its own set of pros and cons. One of the major advantages is its ability to promote weight loss and control blood sugar with fewer doses (once a week), but it can be expensive and is typically prescribed when other treatments have not been effective. On the other hand, Metformin remains the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes due to its proven track record, lower cost, and fewer complications.
Ultimately, the choice between Metformin and Semaglutide depends on individual patient needs and preferences. For many people, starting with Metformin is an effective way to manage type 2 diabetes, and Semaglutide may be considered if additional treatment is necessary.
Additional Benefits and Uses of Metformin
Metformin has also shown promise in treating other conditions outside of diabetes management. For instance, it is sometimes prescribed for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition that affects a woman’s hormonal balance. By improving insulin resistance, Metformin can help restore normal ovulation in women with PCOS, increasing their chances of becoming pregnant.
Additionally, there is emerging evidence that Metformin may play a role in longevity. Some studies suggest that Metformin could have anti-aging effects, potentially reducing the risk of age-related diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases. While more research is needed in this area, the preliminary findings are promising.
Taking Metformin: What You Need to Know
For most patients, Metformin is taken orally in the form of a pill, usually once or twice daily with meals to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. The dosage will vary depending on the individual’s condition, but doctors typically start with a low dose and gradually increase it to minimize side effects.
It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure that the medication is working as intended. Metformin should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise routine for optimal blood sugar control.
Managing Side Effects of Metformin
As mentioned earlier, some people experience gastrointestinal side effects when starting Metformin, such as nausea, diarrhea, or stomach upset. These side effects are often temporary, but if they persist, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. In some cases, switching to an extended-release form of Metformin can help reduce these symptoms.
If you experience more severe side effects such as muscle pain, weakness, or difficulty breathing, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately, as these could be signs of a rare but serious condition called lactic acidosis.
A Promising Medication for Many
Metformin has remained a trusted and effective treatment for type 2 diabetes for many years. With its ability to manage blood sugar levels, promote modest weight loss, and improve insulin sensitivity, it is a go-to choice for healthcare providers worldwide. Moreover, its affordability and relatively mild side effect profile make it a favorable option for long-term use.
While there are alternatives like Semaglutide, which may offer additional benefits such as more significant weight loss, Metformin’s proven track record ensures that it will remain a first-line therapy for many individuals with type 2 diabetes. The choice between Metformin and other treatments should always be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering the individual’s unique needs and circumstances.
FAQ
Q1: Can Metformin be used for type 1 diabetes? No, Metformin is not effective for type 1 diabetes. It is primarily used for type 2 diabetes, where insulin resistance is the main issue.
Q2: How long does it take for Metformin to work? Metformin typically starts working within a few days, but it may take several weeks to see significant improvements in blood sugar levels.
Q3: Is Metformin safe for long-term use? Yes, Metformin is considered safe for long-term use in most people, though it is important to have regular check-ups to monitor for any potential side effects.
Q4: How does Metformin compare to Semaglutide for weight loss? Semaglutide may be more effective for weight loss compared to Metformin, but Metformin is a more established and affordable option for managing blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes.